How to Choose the Right Data Collection Method for Your Needs
Choosing the right data collection methods is essential for successful market research. It’s important to match methods with research objectives, as well as consider factors such as data type and target audience. Using a combination of methods, like surveys and interviews, helps ensure the accuracy and validity of the data, leading to more informed decision-making.
Contents
- Understanding Different Types of Data Collection Methods
- Factors to Consider When Choosing the Right Data Collection Method
- Top Tools for Various Data Collection Methods
- Combining Data Collection Methods for a Comprehensive Analysis
- Data Collection from Websites for Market Research
Selecting the right data collection method is crucial for ensuring the quality and relevance of your research. Using inappropriate techniques can lead to inaccurate, incomplete, or biased data, which negatively affects your findings.
It’s important to evaluate the available data collection methods and choose the ones that align with your research goals and the type of data you need.
For instance, if you’re studying consumer opinions, qualitative methods like interviews or polls are often effective. On the other hand, to measure market trends, surveys or statistical analysis are more suitable.
By thoughtfully selecting the appropriate data collection methods, you ensure that your data is reliable, valid, and useful for drawing meaningful conclusions.
Understanding Types of Data Collection Methods
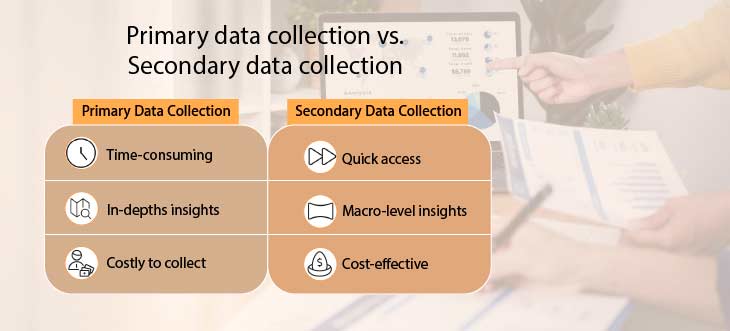
Understanding the various methods of data collection is essential for choosing the right approach to suit your needs. In this section, we explore the different techniques for gathering both primary and secondary data.
Primary Methods of Data Collection
Primary data collection involves gathering firsthand information directly from the source.
Quantitative Approaches
Quantitative methods focus on collecting numerical data, which helps measure and analyze trends, answering questions like “How many?” or “How often?”
- Time Series Analysis: This method involves collecting data at consistent intervals to identify trends, cycles, and seasonality. It is especially useful for forecasting and understanding how variables change over time. For instance, analyzing website traffic can help identify peak seasons.
- Smoothing Techniques: Techniques like moving averages or exponential smoothing help reduce noise and reveal underlying patterns, particularly useful in volatile data.
- Barometric Method: By tracking leading indicators such as building permits or consumer confidence indices, this method helps predict market changes.
Qualitative Approaches
Qualitative methods explore experiences and the reasons behind behaviors and opinions, answering questions like “Why?” or “How?”
- Surveys: Structured data collection from large samples to capture opinions and behaviors using a mix of question formats. This provides both quantitative and qualitative insights.
- Polls: Polls measure public opinion on specific topics and provide immediate feedback. For example, polls can be used to understand customer preferences for a new product feature before it’s launched.
- In-Depth Interviews: These one-on-one sessions delve into individual experiences and motivations. For example, interviewing users who have abandoned shopping carts can reveal usability issues that affect website design.
- Focus Groups: These group discussions help uncover collective attitudes and beliefs within a target group, revealing insights that might not emerge in individual interviews.
- Delphi Technique: A systematic method of gathering expert opinions through multiple rounds of questionnaires to build consensus on a specific topic.
Secondary Methods of Data Collection
Secondary data collection involves using already gathered and compiled data, providing a cost-effective and efficient way to obtain insights.
- Public Databases: Government resources like the U.S. Census Bureau and the Small Business Administration provide extensive, free-access databases on demographics, economic indicators, and industry trends, offering a macro-level view of market landscapes.
- Commercial Market Research Reports: Specialized firms gather and analyze market data segmented by industry, demographics, and consumer behavior. These reports provide in-depth analysis and actionable insights. For instance, Nielsen reports cover market share, brand loyalty, and consumer purchasing behavior.
- Financial Data Sources: Publicly traded companies release financial performance data in quarterly and annual reports. Analyzing these reports helps assess company performance, industry trends, and economic indicators. SEC filings through EDGAR can be used to compare a company’s financial health with its industry peers.
- Internal Company Documents: Sales reports and customer feedback surveys are valuable sources of data for understanding customer behavior, product performance, and market trends. Mining this data reveals insights into customer preferences and areas for improvement within the organization.
- Online Resources through Web Scraping: Web scraping services allow the extraction of data directly from websites. This method helps gather data such as product prices from e-commerce sites, news articles from online publications, or customer reviews using techniques like social media listening. For example, scraping real estate listings from sites like Zillow or Redfin can help analyze housing prices, property features, and location trends to inform market analysis and investment decisions.
Make your sales and marketing effective with our data appending.
Factors to Consider While Choosing the Right Data Collection Method
Selecting the right data collection method requires considering the following key factors. By carefully evaluating these aspects, you can ensure that the chosen method aligns with your business goals and available resources.
Nature of Research
The research objective plays a key role in determining the appropriate data collection approach. Exploratory research, which aims to understand a phenomenon rather than test a hypothesis, typically uses qualitative methods such as focus groups or in-depth interviews to gather rich, detailed data. In contrast, conclusive research seeks definitive answers, often employing quantitative methods like surveys and structured observations to generate statistically analyzable data.
Type of Data Needed
The type of data required influences the choice of methodology. Quantitative data, often numerical, is ideal for measuring trends and identifying patterns. To collect this type of data, large-scale surveys and structured questionnaires are commonly used. Qualitative data, which offers deeper insights into consumer behavior and motivations, is better captured through focus groups, in-depth interviews, and ethnographic studies. Mixed-methods research combines both quantitative and qualitative approaches for a more comprehensive understanding.
Target Audience & Sample Size
Clearly defining the target audience and determining the required sample size are essential for selecting the right method. For niche markets or smaller sample sizes in exploratory research, methods like focus groups or in-depth interviews are valuable for obtaining detailed insights. Larger sample sizes often require more structured methods like surveys.
Budget and Resources
Your budget and available resources will influence the data collection method chosen. Online surveys and data scraping are cost-effective options for gathering data, while face-to-face interviews and focus groups require more resources but provide richer, more nuanced data. It’s important to strike a balance between cost considerations and the need for in-depth insights.
Time Constraints
The project timeline also impacts the choice of research methods. Longitudinal studies, which track trends over time, require a significant time commitment. If immediate insights are needed, real-time data collection methods like social media monitoring or online surveys may be more appropriate.
Top Tools Used for Different Data Collection Methods
It is crucial to choose the right tools for effective data collection in market research. Below is a table listing some top tools categorized by data collection methods:
| Data Collection Method | Tool | Use |
|---|---|---|
| Surveys | SurveyMonkey | Popular for its advanced features like branching logic and skip patterns. |
| Qualtrics | Offers robust survey design, distribution, and analysis capabilities, suitable for complex research needs. | |
| Interviews | Zoom | Facilitates online video conferencing for remote interviews, allowing for face-to-face interaction. |
| Otter.ai | Provides AI-powered transcription, making it easier to analyze interview recordings. | |
| Focus groups | Google Meet | Enables online focus group discussions with screen sharing and recording features. |
| FocusVision | Specializes in focus group management, including participant recruitment and video streaming. | |
| Observation and field data collection | dScout | Enables in-context research by capturing real-time customer experiences through mobile ethnography. |
| Lookback | Facilitates user experience research by recording user interactions and gathering feedback on digital products. | |
| Data analysis tools | SPSS | A powerful statistical analysis software for complex data analysis and modeling. |
| NVivo | A qualitative data analysis software for managing and analyzing textual data like interview transcripts. | |
| General data collection and management | Airtable | Combines spreadsheet and database functionalities for organizing and collaborating on data. |
| Google Sheets | For collaborative data collection, analysis, and visualization. |
Combining Data Collection Methods for a Holistic Understanding
To truly grasp the complexity of any phenomenon, consider combining data collection methods. This strategy allows you to harness the strengths of various approaches while mitigating their individual limitations. Here are some key techniques:
Sequential Explanatory Design
Begin by collecting quantitative data. Then, gather qualitative data to shed light on the initial results.
Instead of merely describing the “what” with qualitative data, delve into the “why” behind unexpected quantitative findings.
For instance, if a survey reveals an unexpectedly high satisfaction rate with a service, conduct follow-up interviews to understand the specific factors driving this satisfaction.
Sequential Exploratory Design
Reverse the approach by starting with qualitative data to explore a phenomenon. Subsequently, utilize quantitative data to generalize these findings to a larger population. Leverage the initial qualitative phase to develop a novel measurement tool or framework.
For example, conduct interviews to understand how individuals perceive “community well-being.” Use these insights to create a quantitative survey instrument for measuring this concept within a broader population.
Concurrent Triangulation Design
Gather both quantitative and qualitative data simultaneously. Compare these data to validate your findings and enhance the robustness of your conclusions.
Go beyond simple comparison and utilize the qualitative data to uncover the mechanisms driving the quantitative relationships. For instance, if a survey indicates a correlation between income and health, conduct interviews to understand how higher income contributes to better health outcomes (e.g., access to healthcare, healthier food choices).
Embedded Design
Nest one data collection method within another to provide a richer, more nuanced understanding of the phenomenon under investigation.
Utilize qualitative data to enrich a primarily quantitative study by capturing the “lived experiences” behind the numbers. For example, in a clinical trial evaluating a new drug, incorporate patient diaries or interviews to understand how the treatment impacts their daily lives and overall well-being.
Multiphase Design
Conduct multiple phases of data collection, with each phase informing the next, allowing for a dynamic and iterative research process. Employ a multiphase design to study a phenomenon over time, capturing both quantitative changes and qualitative shifts in perspectives.
For example, to study the impact of a new policy, we first collect quantitative data on key indicators. Then, conduct qualitative interviews to understand people’s perceptions. Finally, gather further quantitative data to track long-term trends and assess the lasting impact of the policy.
Extract vital web data for smarter business decisions.
Data Collection from Websites for Market Research
Web scraping is an effective method for gathering publicly available data from websites, but dynamic websites that rely heavily on JavaScript can present challenges.
Headless Browsers and AJAX Interception
To tackle these challenges, tools like Puppeteer or Playwright, which are headless browsers, can be used. These tools fully render web pages, including executing JavaScript, making data extraction more efficient. Additionally, AJAX interception allows you to capture data from asynchronous requests.
Advanced Extraction Techniques
For more accurate targeting and extraction of specific data points, advanced techniques like XPath, CSS selectors, and regular expressions can be employed to navigate the HTML structure.
Anti-Scraping Measures and Scaling
Websites often implement anti-scraping measures, so to avoid detection, it’s important to use IP rotation, which involves utilizing multiple IP addresses. In cases where CAPTCHAs are encountered, CAPTCHA solving services can help.
To scale the web scraping process, implement asynchronous requests for parallel processing and distribute tasks across multiple servers or machines.
Ethical and Legal Considerations
Always prioritize ethical and legal standards when scraping. Follow the website’s robots.txt file, apply rate limiting to avoid overloading servers, and ensure compliance with data privacy laws.
Tips for Ensuring Data Accuracy and Validity
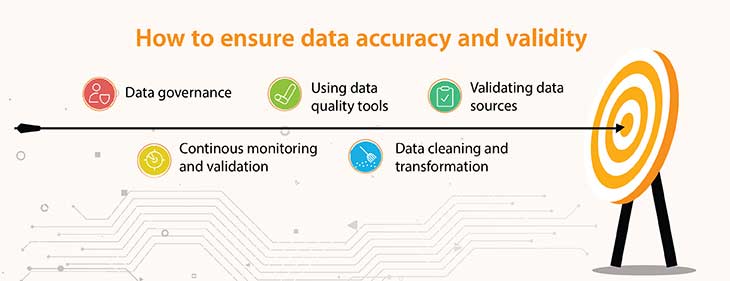
Reliable data is essential for making informed, data-driven decisions that propel your organization forward. Here are some key data validation techniques to ensure the accuracy and dependability of your collected data:
Validating Data Sources and Integrity:
To ensure the reliability of your data, cross-reference it with trusted, reputable sources. Additionally, apply statistical methods to identify outliers and anomalies that could compromise data quality.
Data Cleaning and Transformation:
Before analysis, standardize data formats, correct obvious errors, and address missing values. Strategies like imputation can be used to fill in gaps, or incomplete records can be removed when necessary.
Using Data Quality Tools:
Leverage specialized data quality management software. These tools help in profiling, cleansing, and monitoring your data for errors, ensuring continuous data health and consistency.
Continuous Monitoring and Validation:
Establish systems for ongoing data quality checks. Track essential metrics such as accessibility, reliability, validity, and relevance, which reflect the overall health of your data. Automated alerts can help you detect anomalies as they occur.
Data Governance:
Define clear roles and responsibilities related to data management and quality assurance. Implement standardized processes to ensure that all team members understand how data should be handled and maintained.
Looking Ahead:
The future of data collection will increasingly involve AI and machine learning. These technologies can automate and personalize data collection, offering real-time insights through predictive analytics to enhance decision-making.
Choosing the Right Data Collection Methods:
Effective market research requires selecting the right data collection methods based on research objectives, target audience, and available resources. Leading data collection companies consider these factors to gather valuable insights and support informed decision-making. It is also crucial to ensure that your chosen methods align with ethical standards and your overall research goals.


