How B2B Data Appending Fills the Gaps in Your Database
Contents
- Benefits of Data Appending for B2B Businesses
- Understanding B2B Data Appending
- Types of Data that Can Be Appended in B2B
- Identifying Deficiencies in Your B2B Database
- Strategies to Address B2B Database Deficiencies
- Common Indicators of Gaps in Client B2B Databases
- How Data Appending Resolves Information Gaps
- Challenges of B2B Data Appending
- Case Study: Success with Data Appending
- Conclusion
Delivering a dataset to a client only to find that it contains incomplete, outdated, or inaccurate records can be a significant setback. Research shows that B2B data deteriorates at a rate of 2.1% per month, equating to an annual decay of 22.5%. This means nearly a quarter of your database could become obsolete within a year if left unmaintained.
For data aggregators, maintaining data quality is critical to their reputation and the effectiveness of their clients’ marketing efforts. Through B2B data appending, you can enrich datasets by filling in missing information and enhancing data hygiene and accuracy.
B2B data enrichment plays a crucial role in data quality management, providing reliable data for your clients to base business decisions on.
This article examines the benefits of B2B data appending, how it addresses data gaps, the challenges involved, and how improving customer data through appending can elevate your data aggregation services.
How does data appending benefit B2B businesses?

Boost your market research with our targeted data collection.
What is B2B Data Appending?
B2B data appending is the process of enriching existing business datasets by adding missing or supplementary information sourced externally. The goal is to create a more complete, accurate, and up-to-date dataset, which enhances the effectiveness of marketing, sales, and customer relationship management (CRM) efforts.
Incomplete or outdated data can severely impact business operations. Inaccurate contact details and obsolete information lead to communication breakdowns, ineffective marketing campaigns, and wasted time and resources. For data aggregators, poor-quality data undermines credibility, causes client dissatisfaction, and diminishes the value of their services.
The data appending process employs various methods and technologies, including:
- Manual updates: Performed by skilled data specialists to ensure precision.
- Automated tools: Leveraging algorithms and machine learning for efficiency and scalability.
- Third-party services: Specialists in B2B data enrichment providing verified and enriched datasets.
- APIs for real-time updates: Ensuring databases remain accurate and current by integrating real-time data feeds.
Beyond filling gaps, B2B data appending corrects errors, standardizes formats, and ensures consistency across the database, making it a critical tool for maintaining data quality and reliability.
What types of data can be appended in B2B?
Appending these types of data significantly enhances the quality and depth of your B2B databases, allowing for more effective marketing, sales, and customer service strategies.
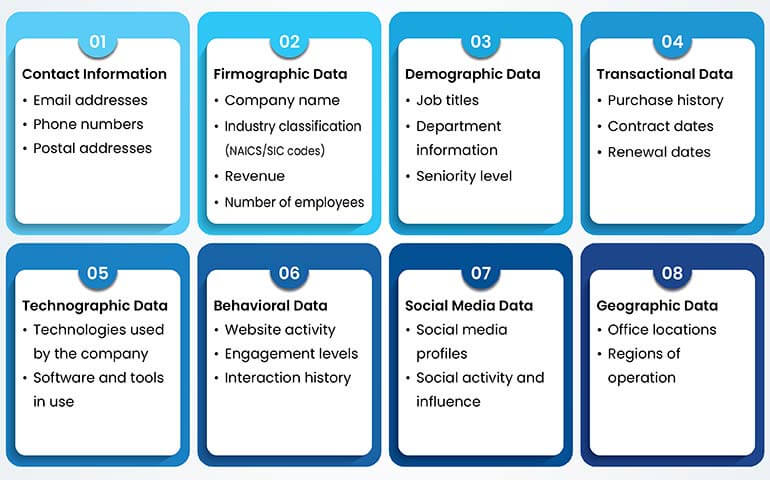
Data appending ensures that databases are comprehensive, accurate, and current, equipping businesses with the reliable information needed to make informed decisions and implement successful marketing strategies.
Make your sales and marketing effective with our data appending.
What are the indicators of deficiencies in your B2B database?
Selling poor-quality sales leads can damage your market reputation and significantly harm your B2B data aggregation business. To avoid these issues, watch for the following indicators:
1. High Volume of Client Complaints
- Indicator: Clients report issues with the accuracy or completeness of the data.
- Cause: Insufficient data collection and validation processes.
- Impact: Lower client satisfaction and potential business loss.
2. Low Match Rates with Client Databases
- Indicator: A low percentage of records match when integrated with client systems.
- Cause: Variations in data standards and formats between the aggregator and client databases.
- Impact: Ineffective data integration, resulting in incomplete records for clients.
3. Outdated Information
- Indicator: Clients frequently find obsolete contact details or outdated company information.
- Cause: Lack of regular data updates or inefficient update mechanisms.
- Impact: Clients make decisions based on outdated data, diminishing the value of the provided data.
4. High Percentage of Incomplete Records
- Indicator: Missing details like contact information, company size, or industry classification.
- Cause: Gaps in data collection or aggregation processes.
- Impact: Clients receive incomplete datasets, hindering their marketing and sales efforts.
5. Poor Data Accuracy Scores
- Indicator: Internal or third-party audits show low data accuracy levels.
- Cause: Inadequate data verification and validation protocols.
- Impact: Loss of client trust and potential reputational harm.
6. High Data Decay Rate
- Indicator: A rapid increase in outdated or unusable data over a short period.
- Cause: Failure to capture fast-changing industry dynamics promptly.
- Impact: Frequent data refreshes are required, driving up operational costs.
7. Client Demand for Data Enhancement Services
- Indicator: Clients frequently request additional data enrichment or cleansing services.
- Cause: Provided data lacks sufficient depth and accuracy.
- Impact: Highlights gaps in the core data offering, signaling the need for enhanced services.
8. Low Utilization of Data Insights
- Indicator: Clients fail to leverage the provided data effectively.
- Cause: Data may lack actionable insights due to gaps in completeness or accuracy.
- Impact: Data underutilization leads to a diminished perception of the value of the services provided.
By addressing these indicators, you can enhance your data appending services and ensure that your offerings remain valuable, accurate, and reliable for clients, thereby protecting your reputation and driving business success.
Explore our data appending services and maximizing your ROI now.
How to address these deficiencies in your B2B database?
To address deficiencies in your B2B database, data aggregators can implement the following strategies:
1. Enhanced Data Collection Methods
- Use diverse sources and advanced techniques to gather more comprehensive and accurate data. This can include tapping into third-party data providers, scraping public records, and leveraging social media insights.
2. Regular Data Updates and Maintenance
- Set up automated systems to ensure your database remains current. This includes periodic data refreshes and real-time updates to maintain accuracy and relevancy.
3. Robust Data Validation Processes
- Implement thorough verification and validation processes. This could involve cross-checking data with trusted sources or using algorithms to detect and correct discrepancies automatically.
4. Data Harmonization Techniques
- Standardize data from different sources to ensure consistency. This means aligning data formats, naming conventions, and classifications across datasets to improve compatibility.
5. Client Feedback Integration
- Actively incorporate feedback from clients to continually enhance the quality of your data. Regular surveys, feedback loops, and open communication can help identify areas for improvement and address data gaps.
6. Advanced Data Enrichment
- Enrich existing records by adding valuable attributes such as firmographics, demographics, and behavioral data. This provides clients with more actionable insights and comprehensive datasets.
7. Automation of Data Processing
- Streamline workflows through automation to improve data processing efficiency and accuracy. Automated tools can handle repetitive tasks like data cleansing, verification, and integration, ensuring consistent results.
8. Continuous Monitoring and Auditing
- Regularly audit and monitor your database to proactively identify and address any gaps or errors. This helps ensure that data remains accurate, complete, and aligned with client expectations.
By implementing these strategies, B2B data aggregators can maintain high-quality, up-to-date databases that meet the needs of clients and support more effective marketing, sales, and business decision-making.
Common signs of gaps in your client’s B2B database
If you, as a data aggregator, fail to maintain proper data hygiene and enrichment, it will negatively impact your clients. They may face problems and quickly recognize that the data provided is ineffective.
| Signs of gaps | Description |
| High Email Bounce Rates | Undelivered emails indicate outdated or incorrect contact info. |
| Low Engagement Rates | Poor open and click-through rates suggest poor audience reach or segmentation. |
| Inaccurate Reporting and Analytics | Discrepancies in performance metrics signal data gaps or errors. |
| Duplicate Records | Multiple entries for the same contact indicate data inconsistency. |
| Incomplete Customer Profiles | Missing key information suggests gaps in customer profiles. |
| Poor Lead Conversion Rates | Low conversion rates point to inaccurate or insufficient lead information. |
| Outdated Information | Frequent changes without updates indicate a need for data maintenance. |
| Customer Complaints and Feedback | Negative feedback highlights inaccuracies in contact data. |
| Inconsistent Data Across Systems | Data variations between systems suggest synchronization issues. |
How B2B data appending addresses these information gaps?
B2B data appending bridges critical information gaps by enriching your database with missing or outdated details, improving data accuracy and completeness. This process supports better decision-making and more effective marketing efforts. Below are examples of how B2B data appending resolves common data issues:
Address Completion
- Adding Missing Address Information: Fills in incomplete physical addresses, enhancing the database.
- Benefits: Accurate geolocation and improved targeted marketing for more effective campaigns.
Email Enrichment
- Appending Missing or Outdated Emails: Ensures email addresses are up-to-date and complete.
- Benefits: Facilitates better communication for marketing campaigns and customer outreach, boosting engagement and response rates.
Phone Number Addition
- Enhancing Direct Communication: Appends phone numbers to provide sales teams with accurate contact information.
- Benefits: Increases lead conversion by making it easier to reach potential clients directly.
Social Media Profiles
- Enriching Customer Profiles: Appends social media profiles to enhance customer data.
- Benefits: Improves social media marketing efforts and customer engagement by providing relevant social media links.
Firmographic Data
- Providing Deeper Insights: Adds firmographic data such as company size and industry.
- Benefits: Enables precise business segmentation and targeted marketing, improving campaign effectiveness.
Demographic Data
- Improving Customer Segmentation: Adds demographic information like job titles and age.
- Benefits: Supports personalized marketing and tailored product offerings, increasing customer satisfaction and conversion rates.
Technographic Data
- Tailoring Marketing Strategies: Appends information about the technologies a company uses.
- Benefits: Enables customized marketing strategies based on the technological landscape of target companies.
Behavioral Data
- Enhancing Customer Engagement: Appends behavioral insights based on customer actions and interactions.
- Benefits: Enhances customer engagement strategies by providing a deeper understanding of customer preferences.
Intent Data
- Driving Proactive Efforts: Appends data showing purchase intent or interest in specific products or services.
- Benefits: Enables proactive sales and marketing targeting potential buyers who show intent signals.
Financial Data
- Assisting in Risk Assessment: Adds financial performance data, such as credit scores.
- Benefits: Supports risk assessment and financial planning by providing valuable economic insights.
Real-Life Example
In a typical scenario, gaps in a client’s B2B database were identified and resolved by appending essential, accurate information. For example, a video communication company improved its marketing by appending relevant customer details, enabling effective upselling, cross-selling, and customer retention. This enhanced sales and boosted overall business performance.
What are the challenges of appending B2B data?
Implementing B2B data appending presents several challenges that must be addressed for effective integration and data management. Here’s a breakdown of these challenges and how to approach them:
1. Data Privacy and Compliance
- Challenge: Ensuring compliance with GDPR, CCPA, and other data privacy regulations is complex. Managing consent and adhering to privacy laws requires careful attention and can delay the appending process.
- Solution: Implement strict compliance protocols, regularly review privacy laws, and use tools that automate consent management. Make sure the data append provider follows these regulations.
2. Data Quality and Accuracy
- Challenge: Incorrect or outdated information can be appended, which undermines database reliability.
- Solution: Vet data sources for quality and accuracy before appending. Implement data validation checks and cross-referencing techniques to verify the information.
3. Integration Issues
- Challenge: Appending data to existing systems like CRM, ERP, or marketing platforms can be technically difficult due to differences in data formats.
- Solution: Use specialized integration tools or hire experts to ensure that the appended data fits seamlessly into existing platforms. Data mapping and transformation tools can help in aligning the formats.
4. Cost Considerations
- Challenge: Data appending services can be costly, and calculating ROI can be difficult in the short term.
- Solution: Evaluate the long-term benefits of having accurate, up-to-date data, such as improved marketing ROI and customer engagement. Make sure the investment aligns with your business goals.
5. Data Overload
- Challenge: Handling large volumes of appended data can overwhelm your systems, leading to inefficiencies and poor data management.
- Solution: Prioritize data relevance, ensure that only valuable data is appended, and implement efficient data management practices. Use tools that help filter, sort, and organize appended data.
6. Data Consistency
- Challenge: Ensuring consistency between appended data and existing records is vital to prevent discrepancies.
- Solution: Regularly update and synchronize data across platforms. Set up automatic synchronization processes to maintain data consistency and reliability over time.
7. Quality of Append Providers
- Challenge: The reliability and accuracy of the data append provider are crucial. Selecting the wrong provider can lead to inaccuracies or vendor lock-in.
- Solution: Thoroughly vet potential data append providers for quality, reliability, and adherence to industry standards. Look for reviews, case studies, and compliance certifications.
8. Security Concerns
- Challenge: Data security and confidentiality are at risk during the appending process, especially with sensitive information.
- Solution: Choose providers with robust security measures in place, such as encryption and secure access protocols. Regularly audit data security practices to protect against breaches.
9. Complex Matching Algorithms
- Challenge: Aligning new data with existing records requires accurate matching algorithms, which can be challenging due to data variability.
- Solution: Invest in sophisticated matching algorithms or use machine learning models that can handle data variability effectively. Test algorithms regularly to minimize errors.
10. Scalability
- Challenge: The data append process must be scalable as the database grows, requiring enough resources to handle future expansion.
- Solution: Plan for future data growth and invest in scalable infrastructure and systems. Implement strategies that ensure data management processes can scale seamlessly.
Conclusion:
Addressing these challenges requires careful planning, selecting the right data appending service provider, and creating strong internal processes to ensure the accuracy, security, and compliance of the appended data. By mitigating risks and optimizing the appending process, businesses can maximize the value of their enriched data and enhance their decision-making capabilities.


